Gummy stem blight affects all cucurbits, but in Florida, it is seen more as issue in watermelon and cantaloupe. The disease can cause significant production losses during warm and wet conditions.
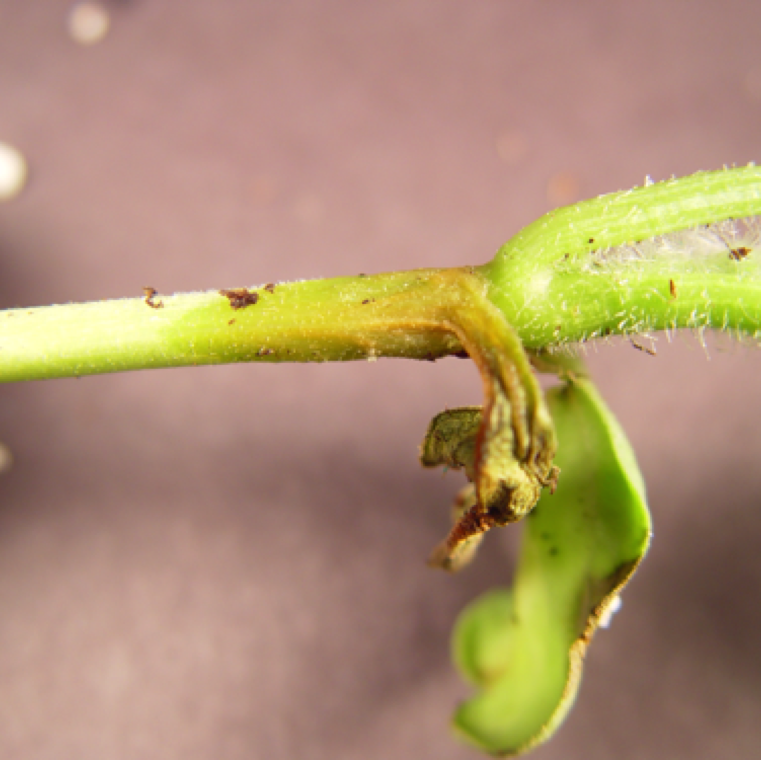

Disease symptoms are often visible before and after transplanting in the field. The stem of transplants same may show water soaking. Wilting of plants followed by death of the transplants can occur.
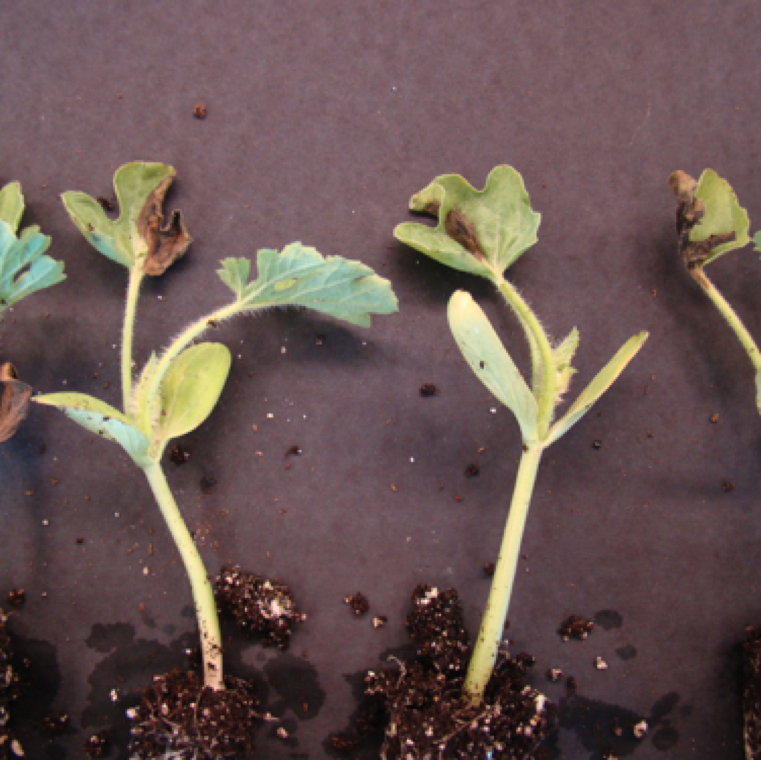

Transplant infection is common and can be due to use of contaminated seed or poor sanitation in the greenhouse. Light- to dark-brown necrotic spots and leaf yellowing are early symptoms.

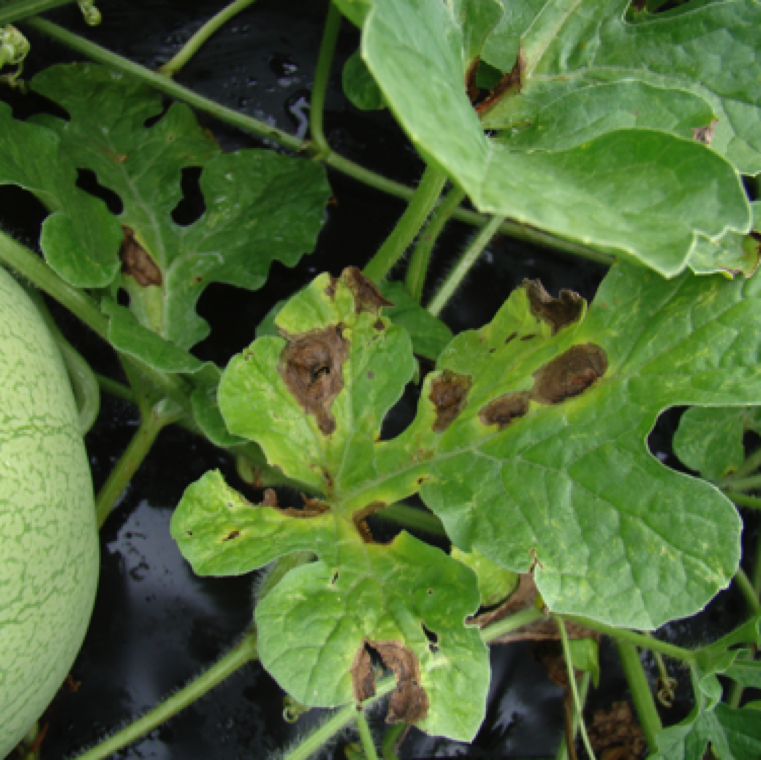
The first symptoms in the field is the necrotic regions which are round or oval with a circular pattern on the leaves where moisture retention is high as seen here on watermelon leaves.

The disease on watermelon can cause major necrosis of the leaves with many lesions merging together within a few days under ideal conditions for the spread of the pathogen.
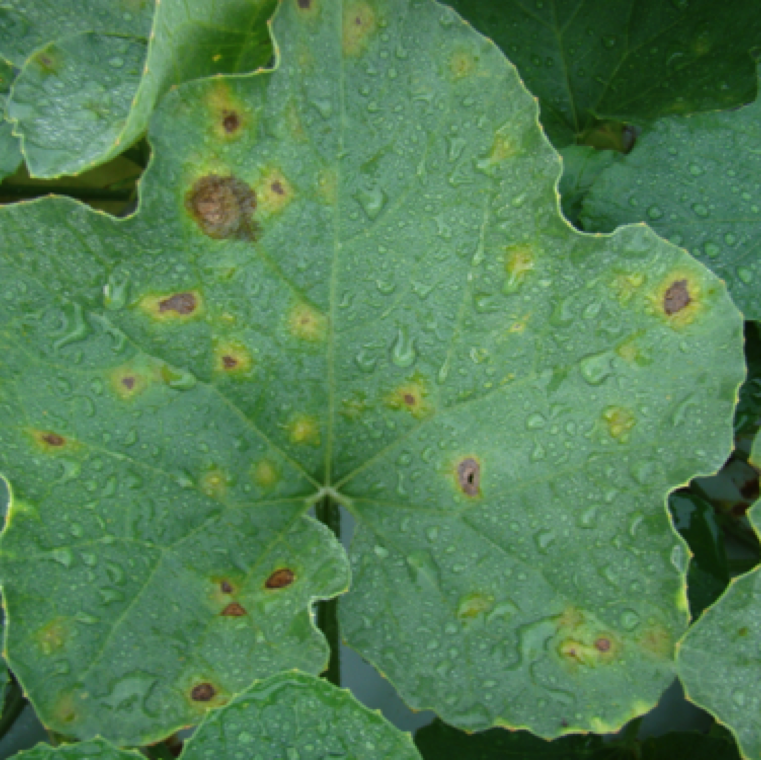

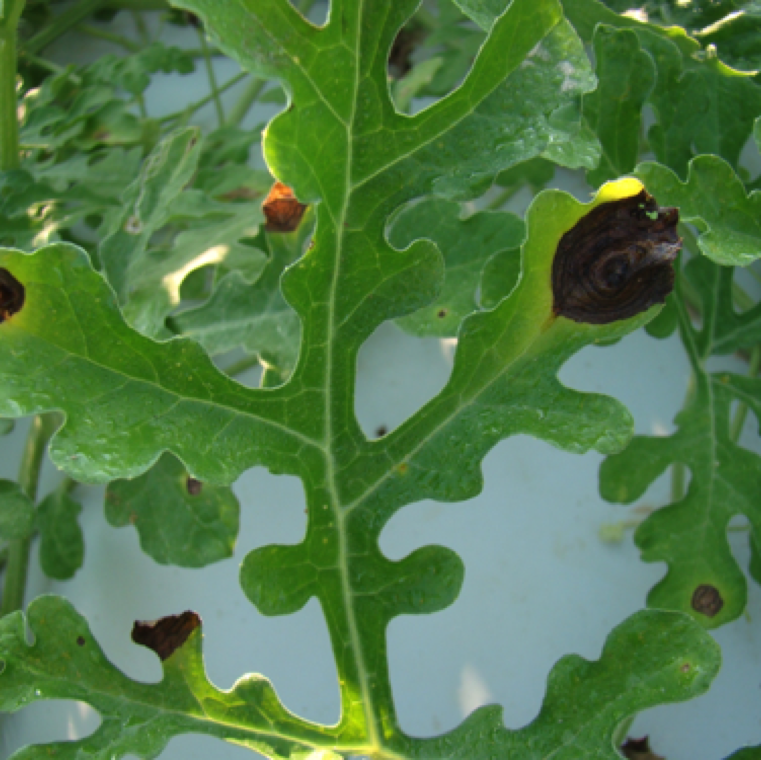
Early stage symptoms on cantaloupe is similar to watermelon. However, lesions tend to be round or irregular In shape. The brown lesions form after formation of small yellow spots.
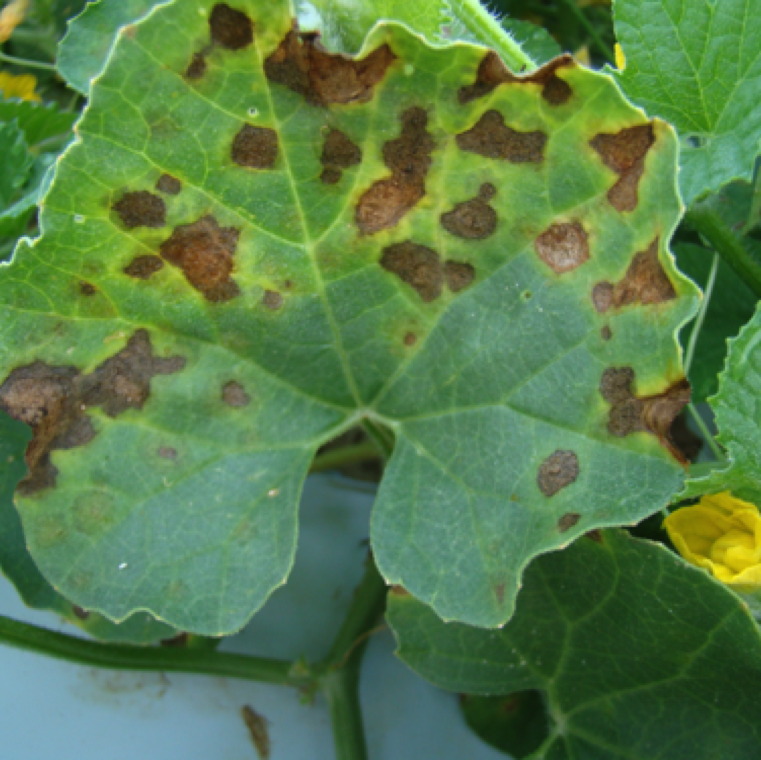

Necrotic spots merge together to form large blighted sections on cantaloupe leaves affecting photosynthesis. The leaves turn yellow rapidly and the disease spreads rapidly under ideal conditions.
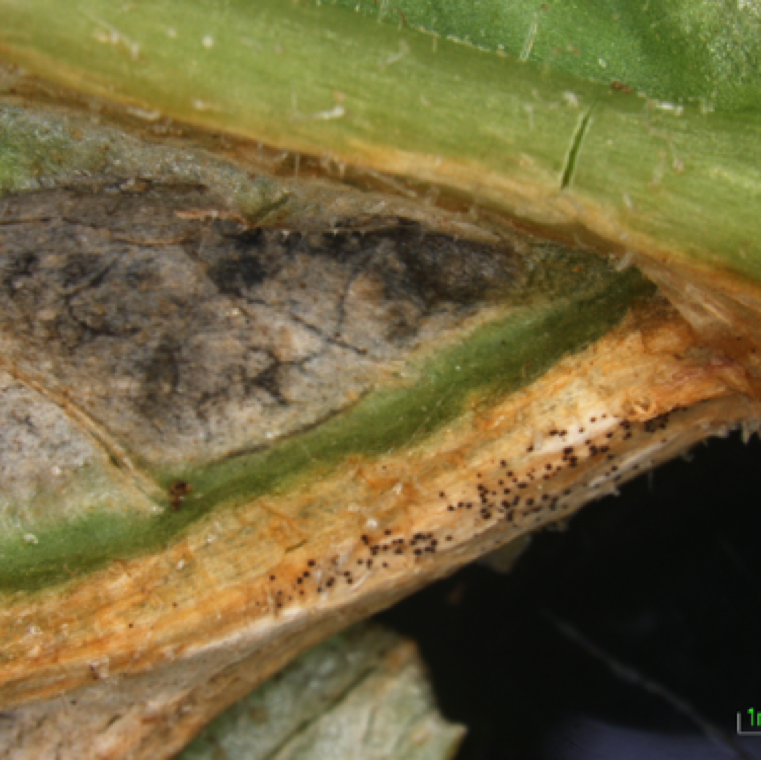

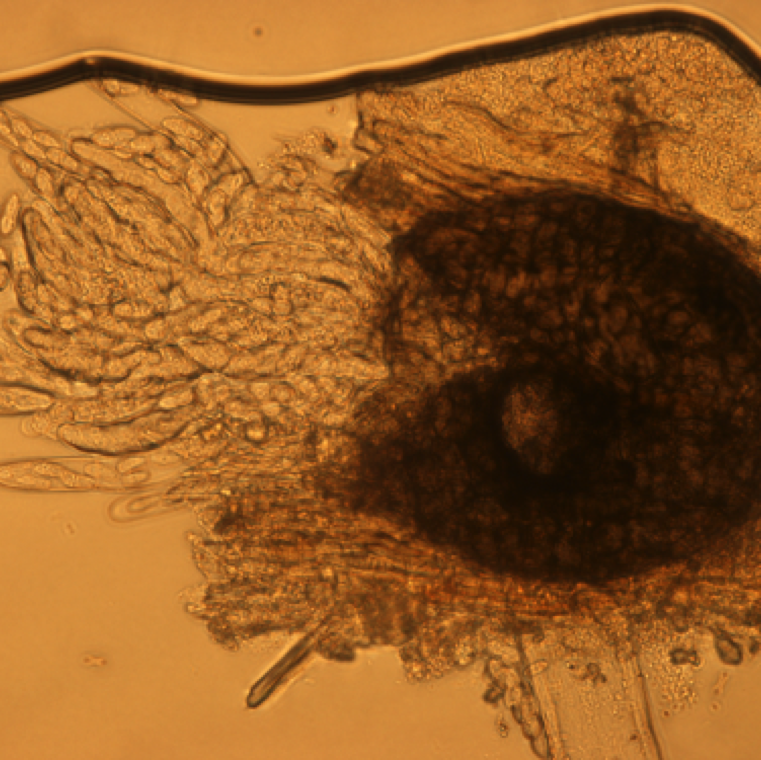
Black fruiting bodies of the fungus (pycnidia, perithecia, or pseudothecia) are often visible on the infected leaves, and serve in confirmatory diagnosis.

Water-soaking on the underside of an infected watermelon leaves is a common symptom. Careful observation of the leaves will indicate black fruiting bodies of the fungus.
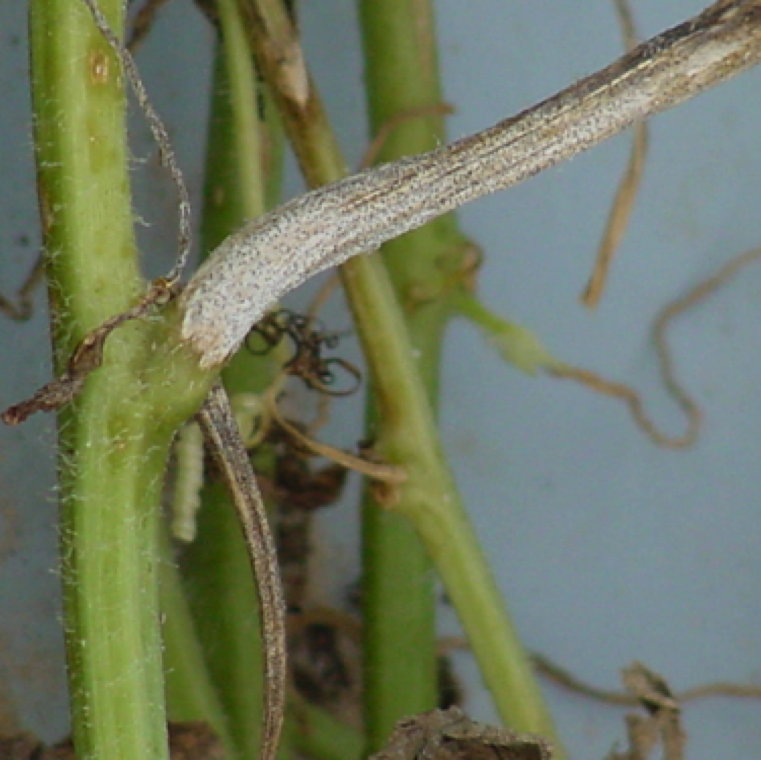

A watermelon vine with numerous black fruiting bodies. These are normally noticed during active infection and disease management becomes extremely difficult.
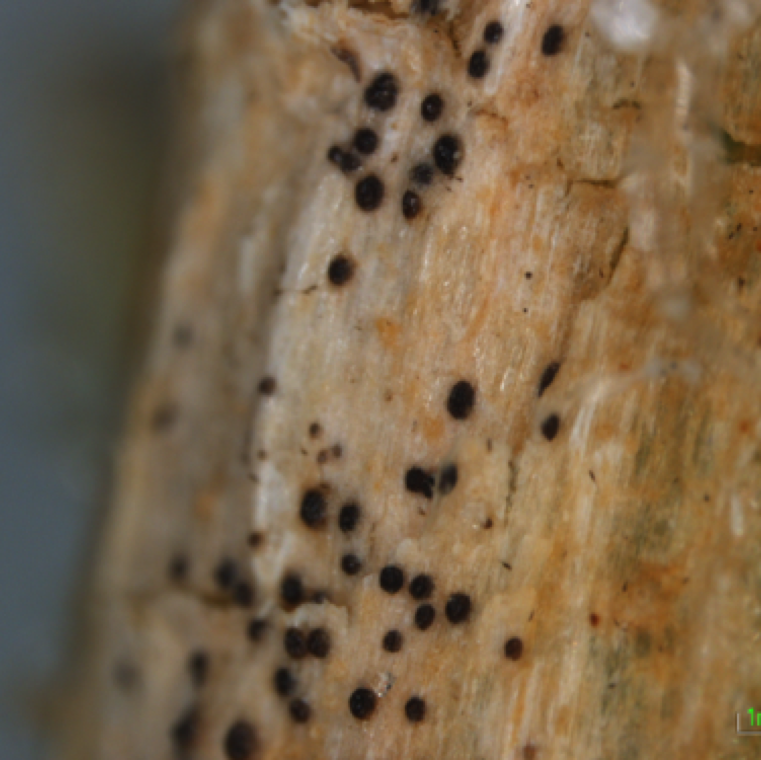

A close-up of black fruiting bodies on watermelon vine infected by gummy stem blight. This is characteristic of gummy stem blight diseases on all cucurbits.
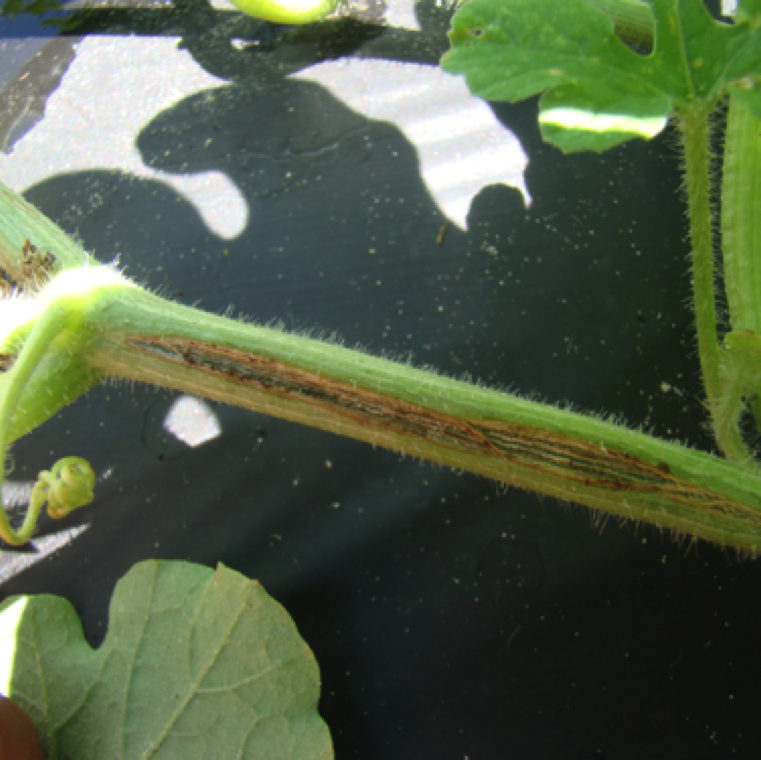

Cankers develop on the stem and cracking of the stem and vines is often visible on affected plants. Cracking can be due to reasons other than gummy stem blight.
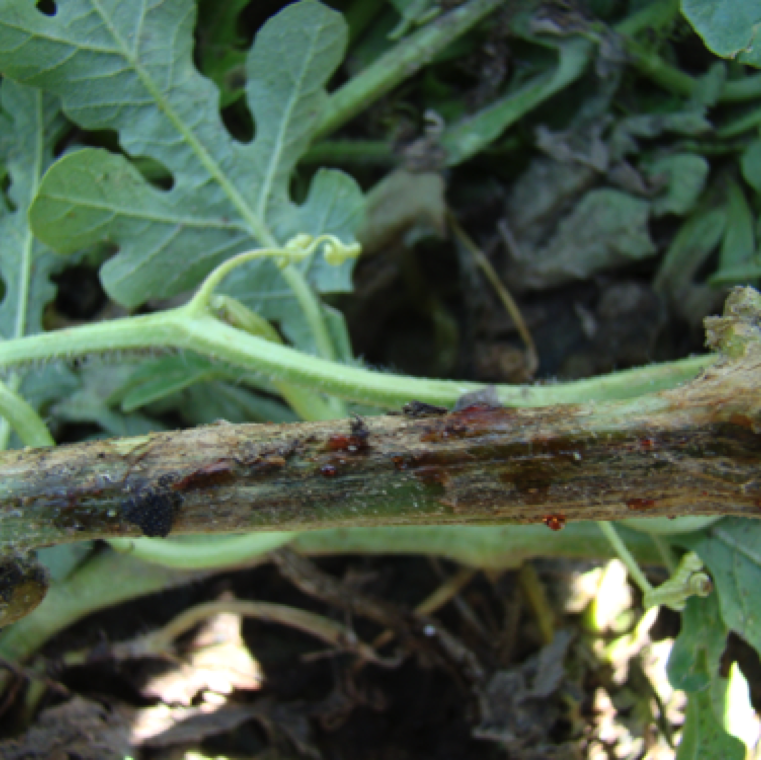

A red to amber gummy substance can exude from infected stem and vines. Anthracnose and inadequate soil liming can also cause the exudation of a gummy substance.
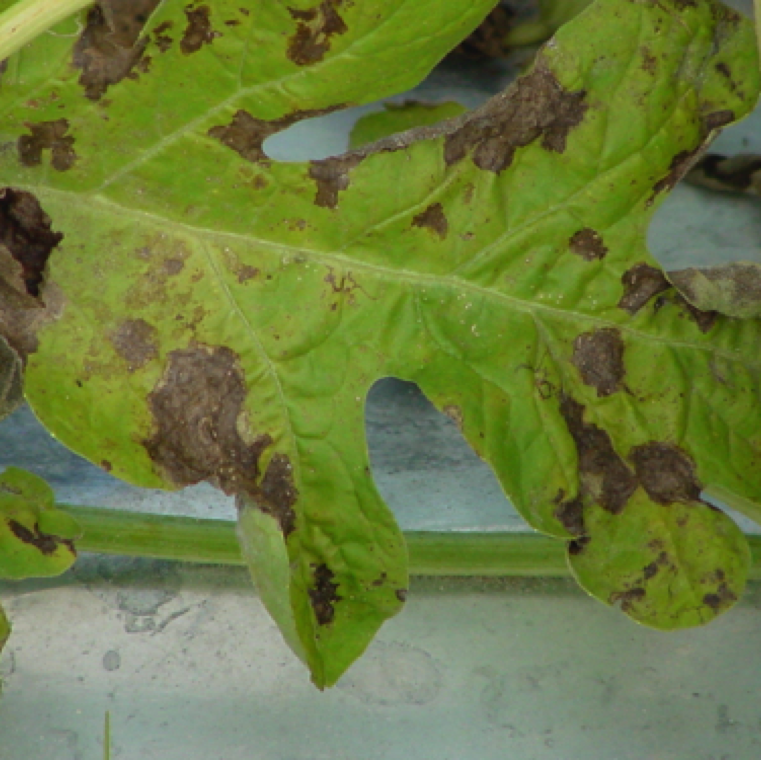

A leaf with severe infection of gummy stem blight with lesions primarily on margin of leaves. The leaves turn brittle and desiccate rapidly exposing fruits to sunburn.
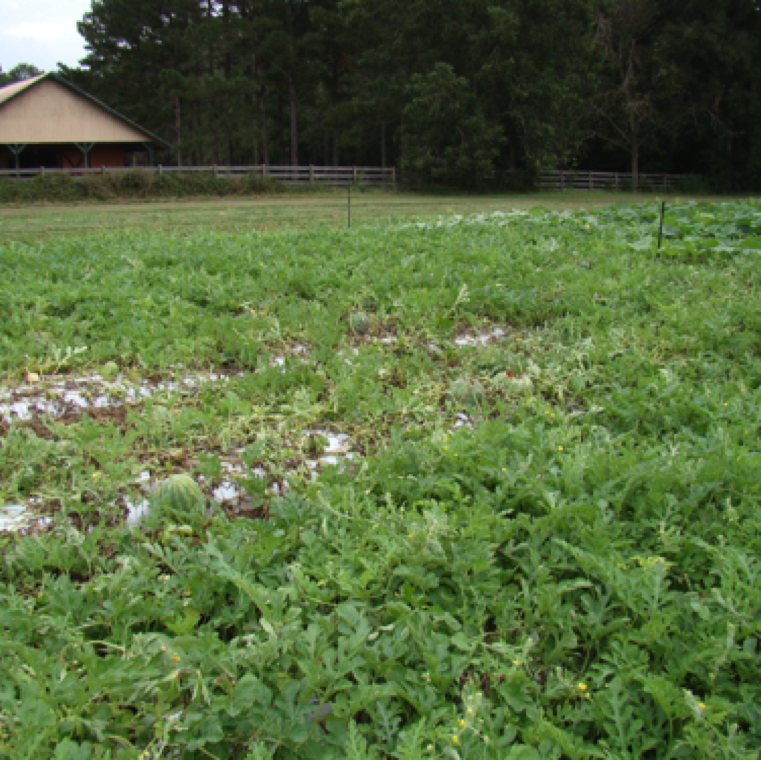

Plants can become infected the disease at any stage of the plant, from seedling to mature vine with fruit. Infection signs and symptoms can be seen on all parts of the plant except roots.
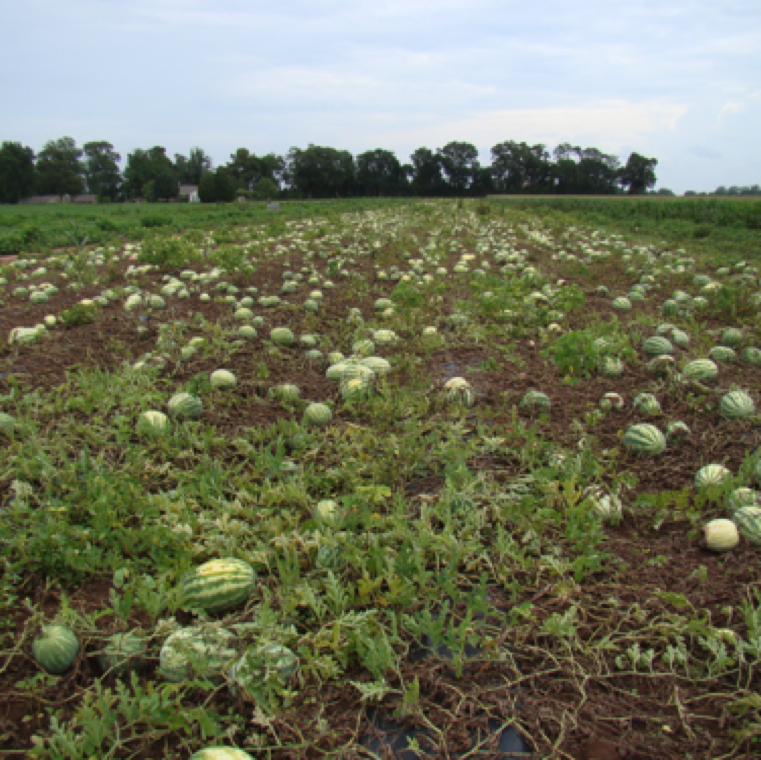

Gummy stem blight can cause severe leaf blighting as seen in this field. The fruits are affected by sunscalding and thus 100% non-marketable fruits.
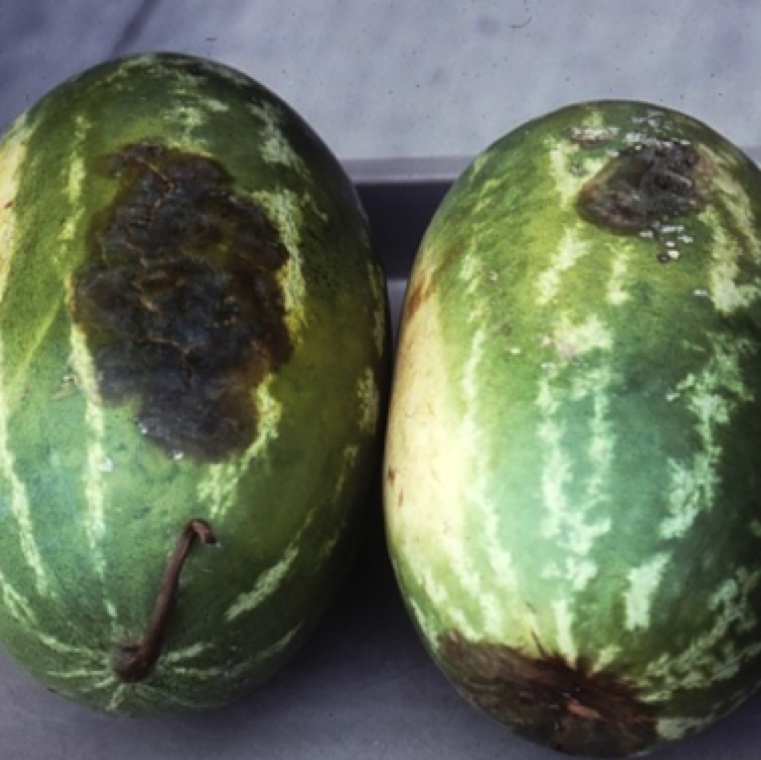

Fruit rot is only a problem if the vines are severely affected. Lesions on watermelon are first oval to circular and greasy green in color. These lesions can be depressed in the center.

Black rot symptoms on honeydew melon are similar tot hat on watermelon. Harvest points on fruits can also be a point of entry for the pathogen, leading to post-harvest decay.
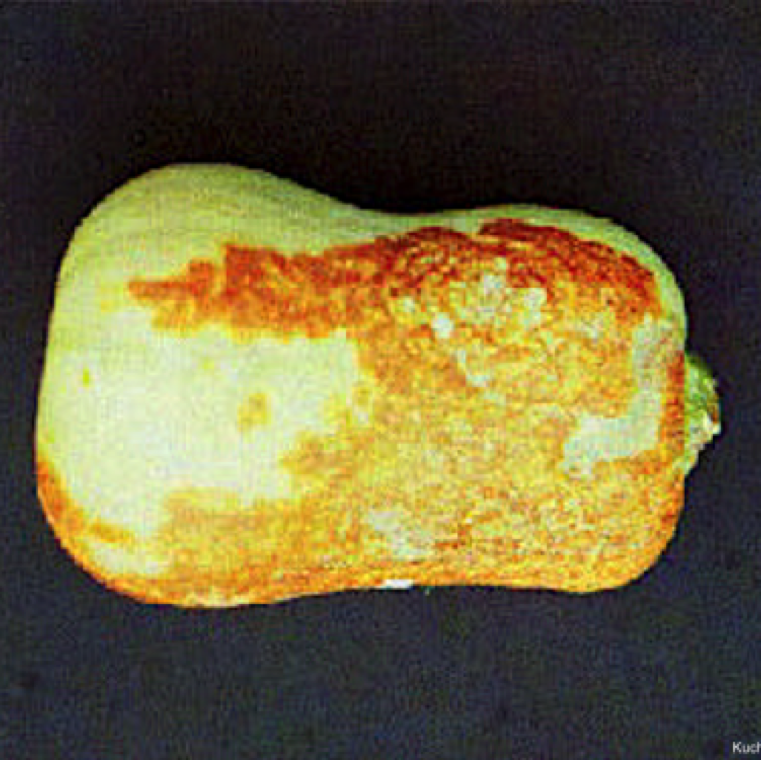

Butternut squash fruits can be infected with even when the vines are healthy. Lesions that are dark yellow to brown in color and crusty in appearance, can be seen on large areas on the fruit.
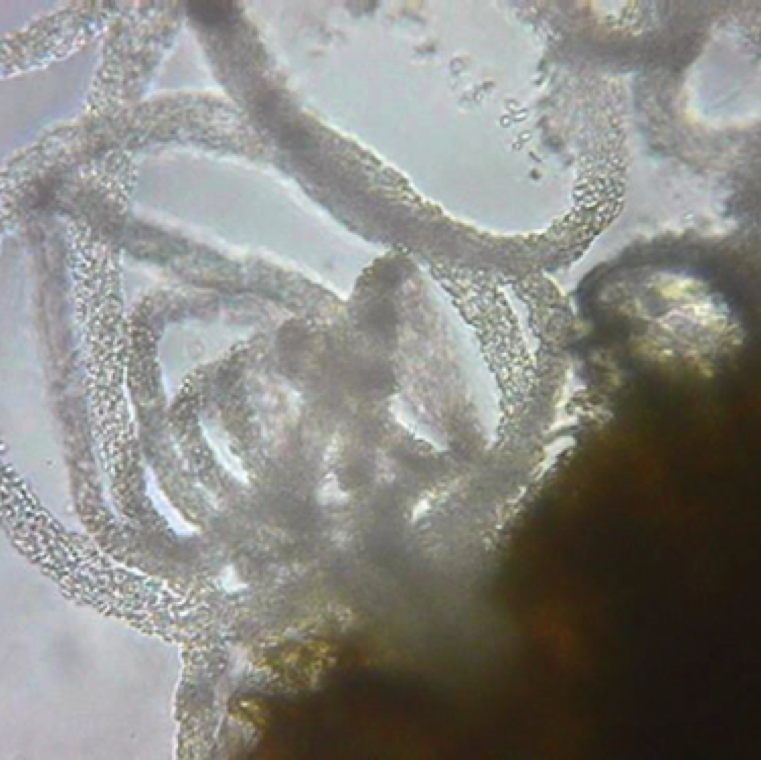
Pycnidia swell and release tendrils of spores if the tissue is wetted in water. This can be easily observed with the use of a microscope. Conidia exuding from pycnidia is in the shape of a "spore horn”
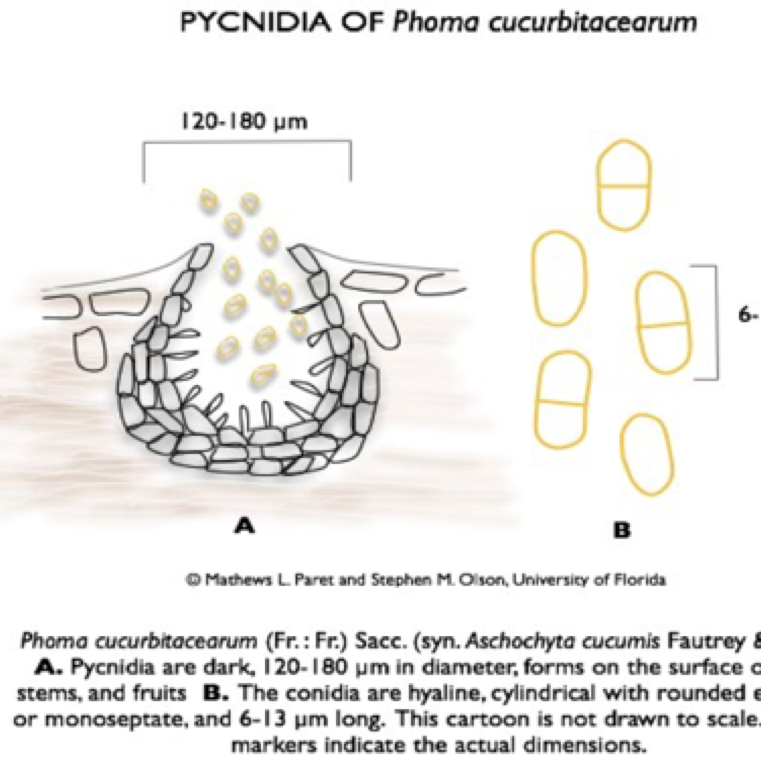
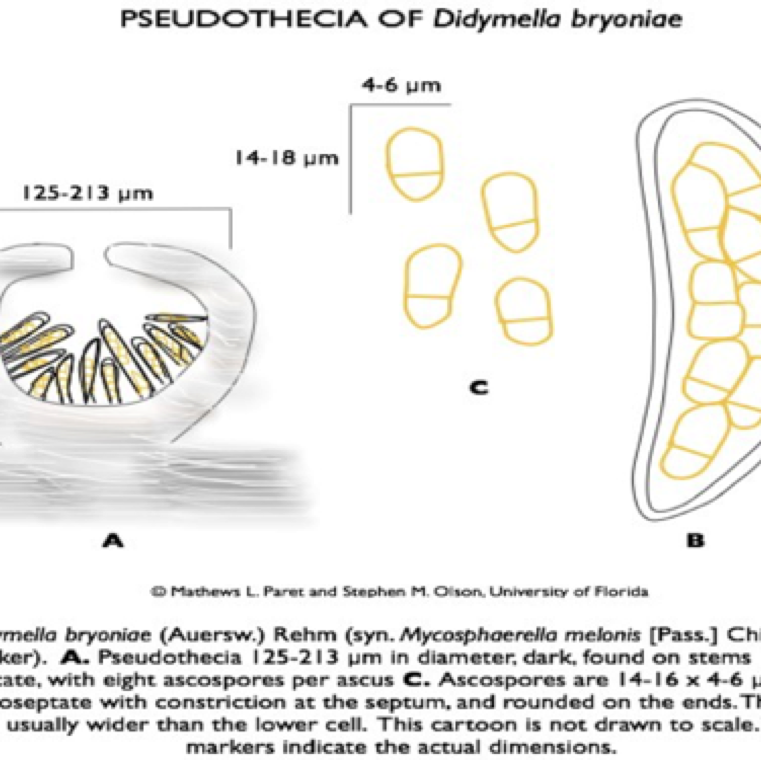
The fungus produces two spore stages, an asexually produced spore (pycnidia giving rise to conidia) and a sexually produced spore (perithecia giving rise to ascospores).
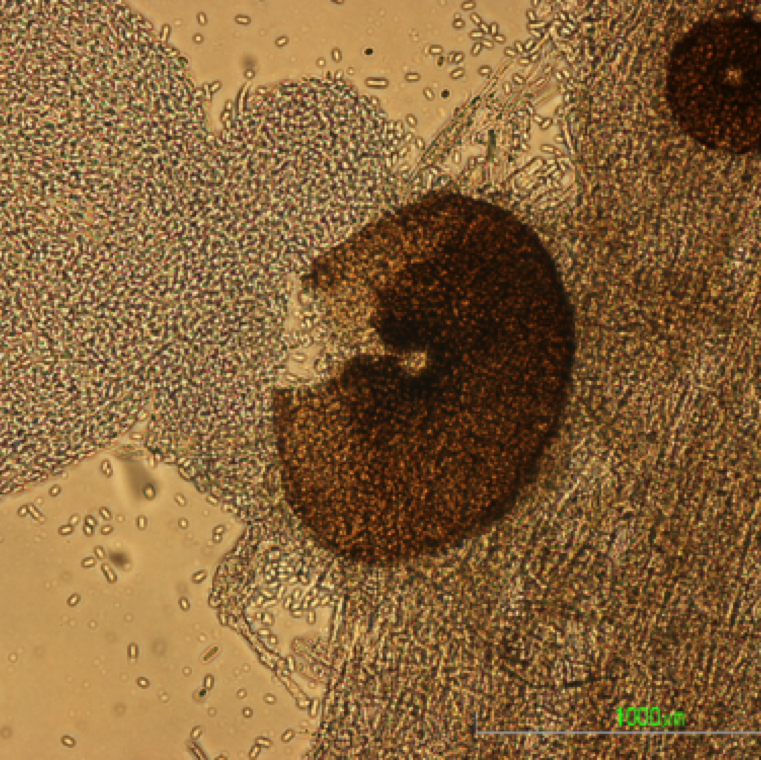
Conidia released from pycnidia embedded on a infected plant tissue. This can be noticed on leaf, stem, and fruit samples and is a useful diagnostic tool in the lab.
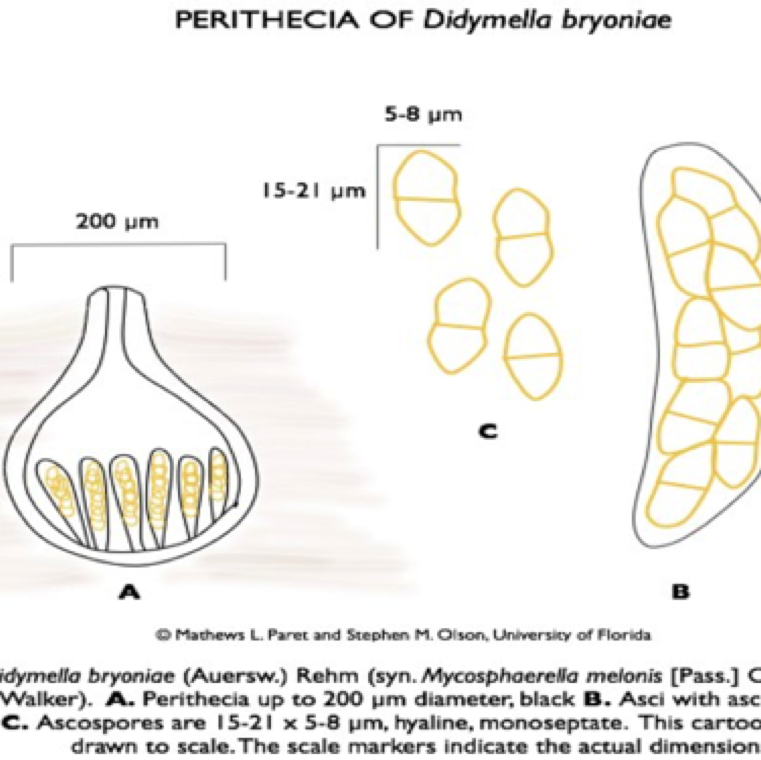
Ascospores serve as the primary inoculum and are readily spread by wind. Conidia are released in a gummy substance and adapted for short-distance movement through splashing water.
GUMMY STEM BLIGHT
Fungal causal agent: Didymella bryoniae (anamorph: Phoma cucurbitacearum)
Cucurbit diseases