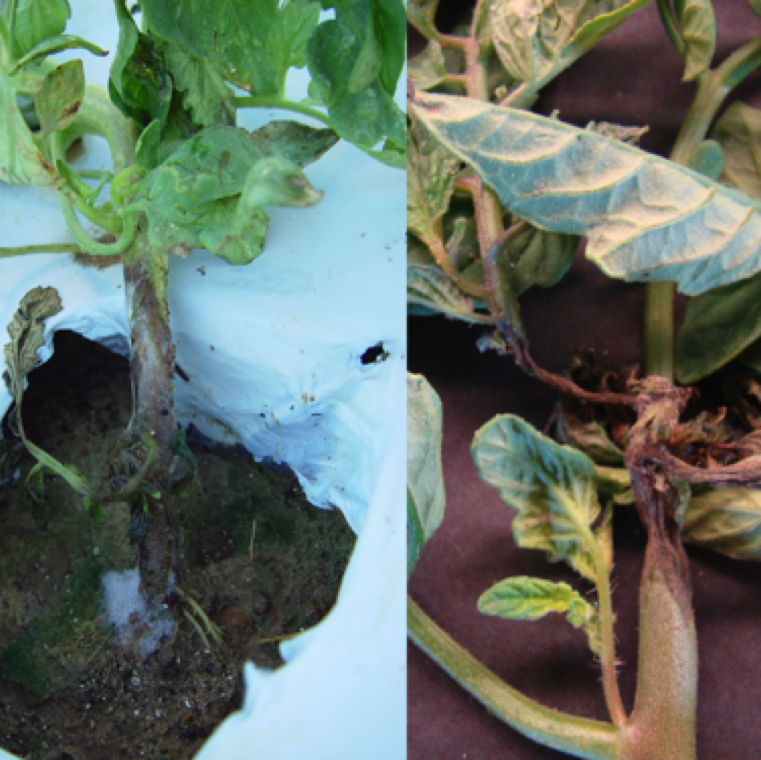
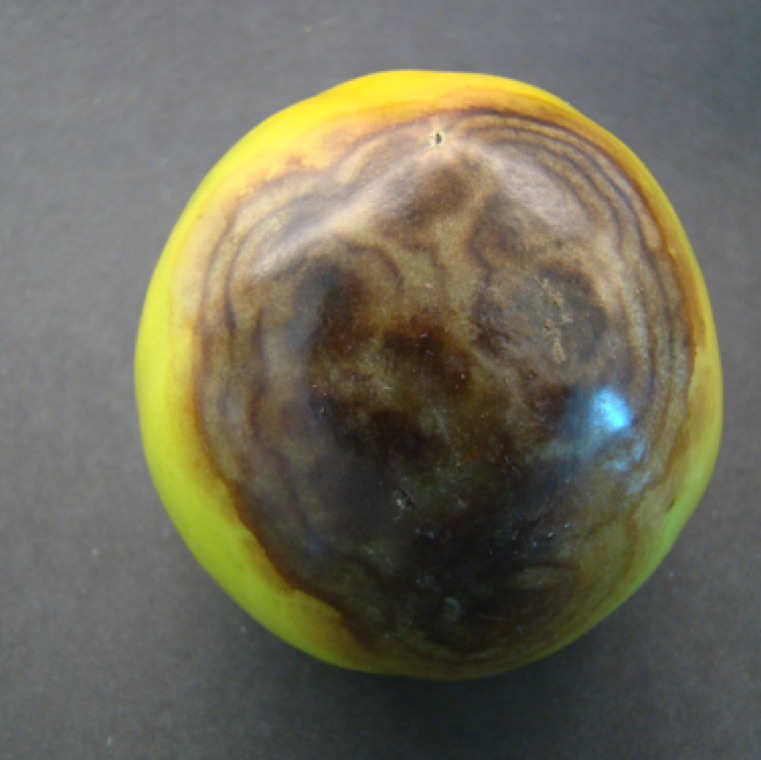
Phytophthora root rot infection on young plants with white cottony growth at crown of the plant and plants show early signs of wilting (left). Watersoaking and necrotic stem can also be noticed (right).
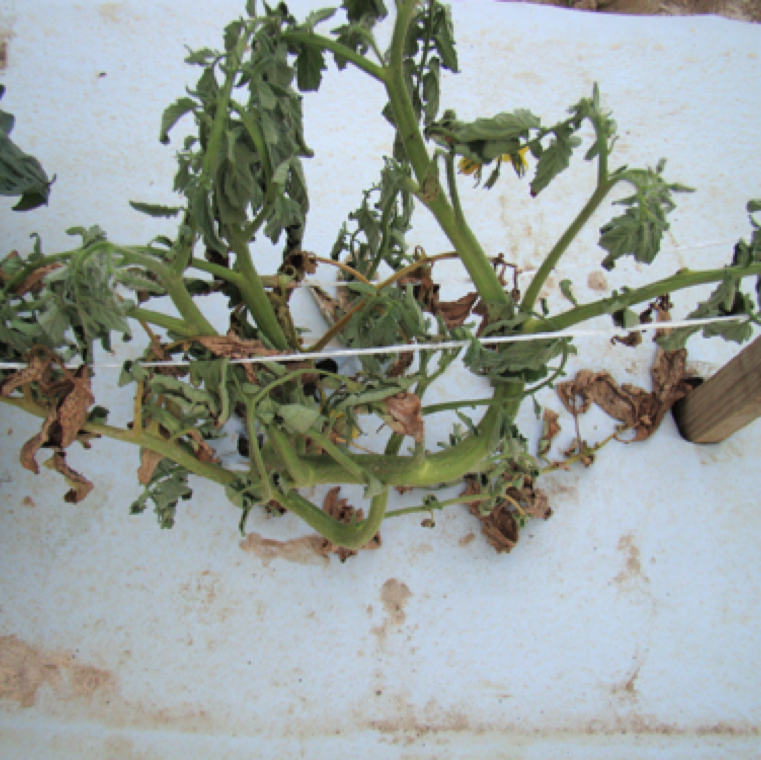

Completely wilted plants due to Phytophthora root rot due to several destruction of roots. Prolonged period of warm wet conditions and heavy soils favor disease occurrence.
BUCKEYE ROT and PHYTOPHTHORA ROOT ROT
Fungal causal agent/s: Phytophthora nicotianae var. parasitica, P. capsici, P. drechsleri (All 3 causes buckeye rot, and first 2 causes root rot)
Tomato diseases