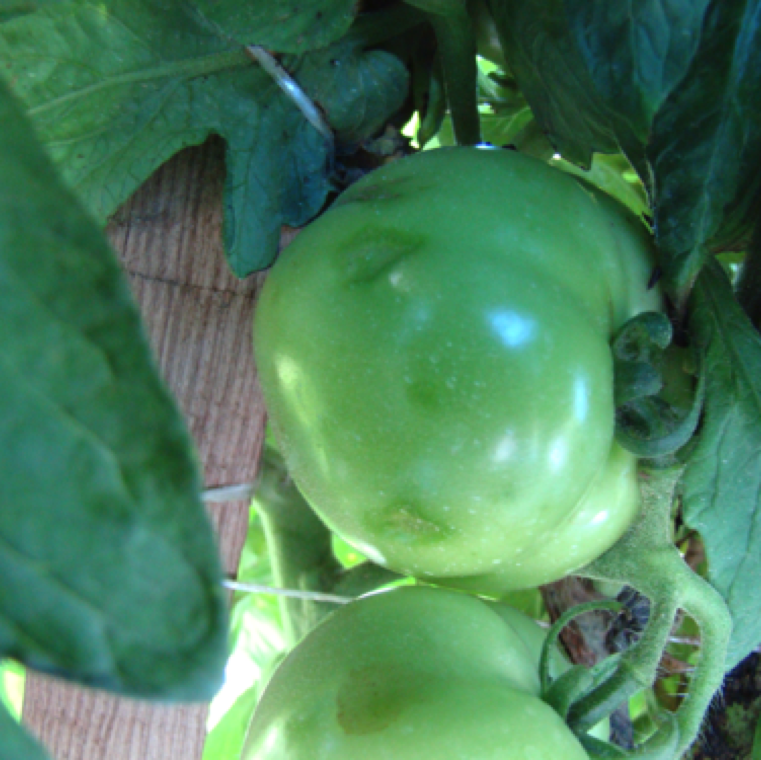
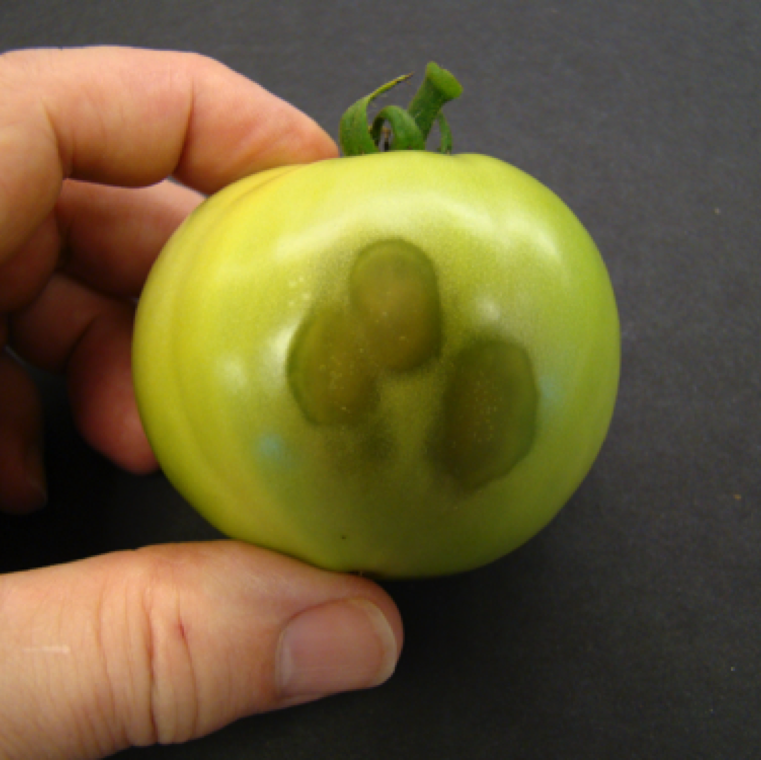
The fruits affected by soft rot shows water-soaked lesions which leads to the collapse of the affected fruits. The bacterium can reside in soil for many years.
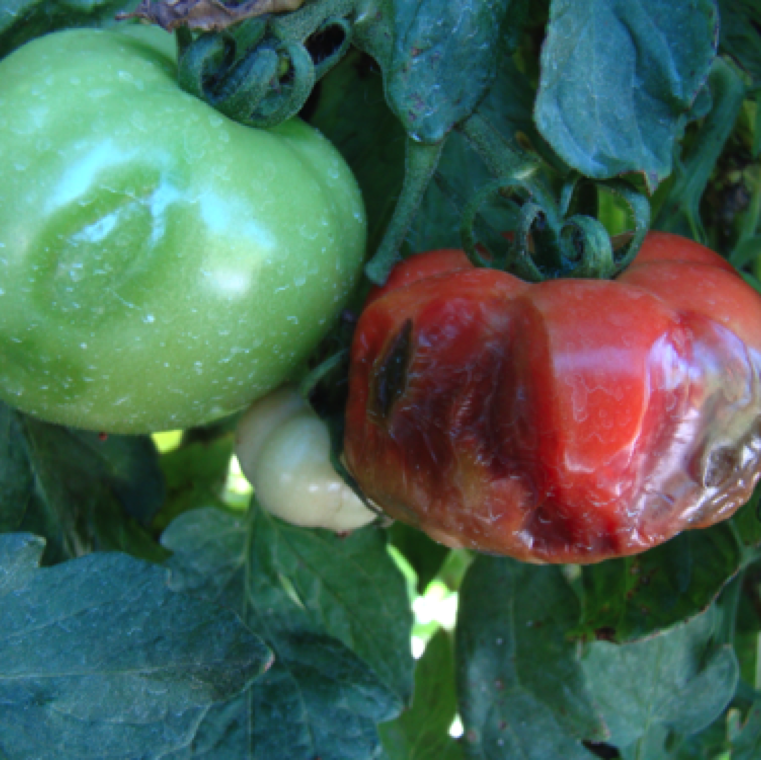

The bacterium can be easily transmitted during pruning operations, splashing of infested soil on to plants with wounds and movement by chewing insects and larvae.
BACTERIAL SOFT ROT
Bacterial causal agent: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora (Pectobacterium carotovorum)
Tomato diseases