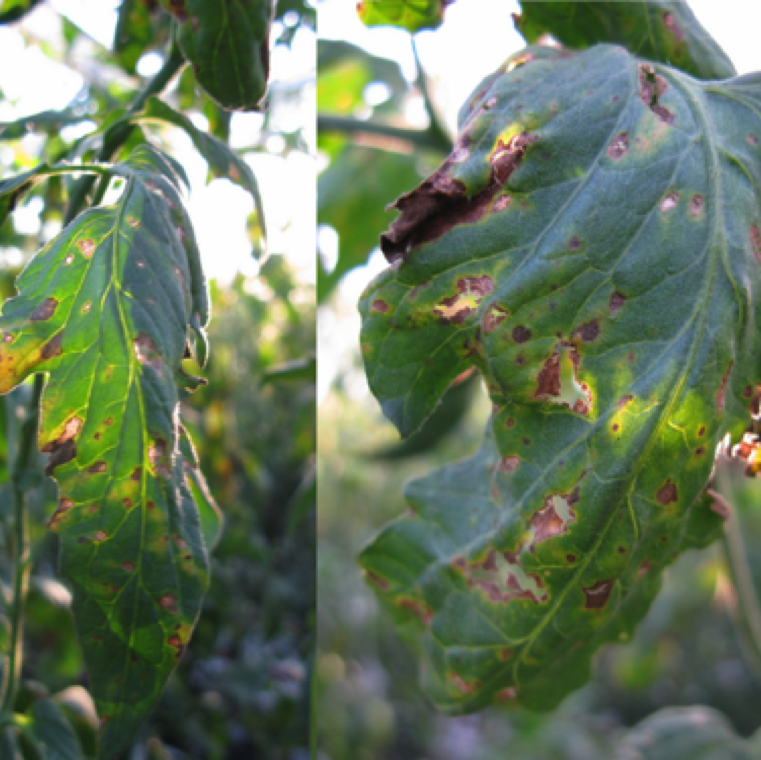
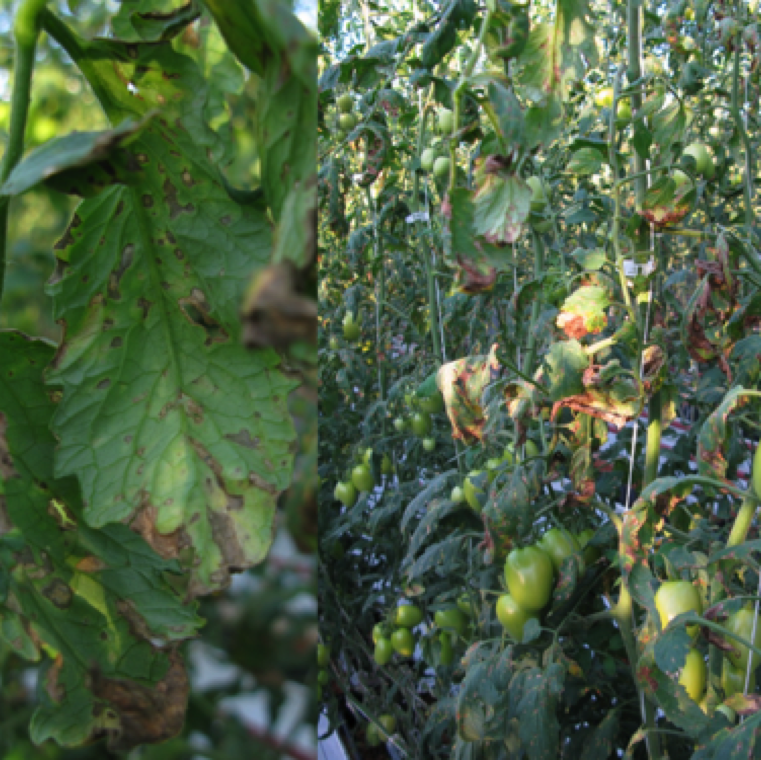
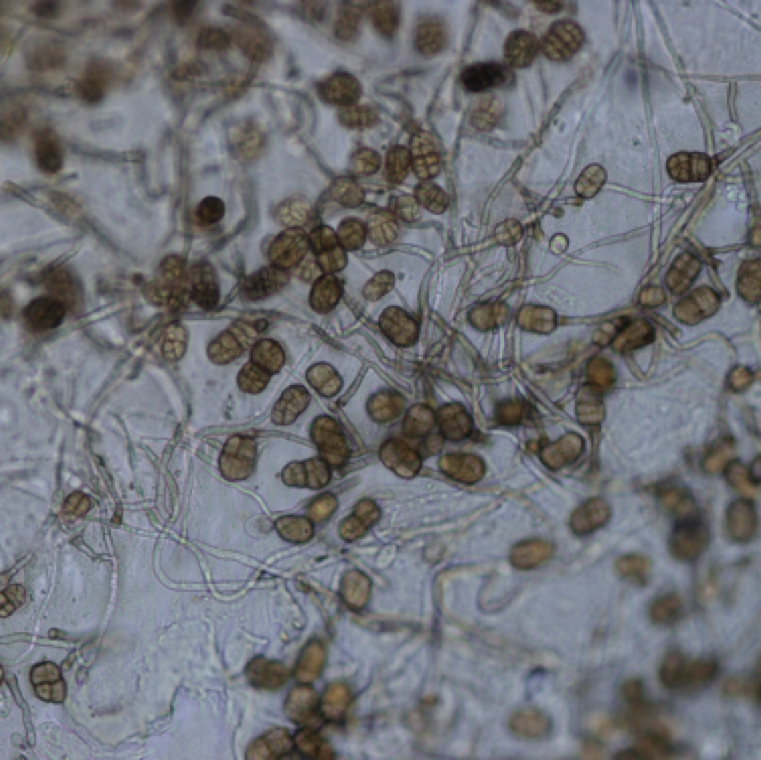
Brown specks scattered through the leaf surface is a characteristic symptom of gray leaf spot. These specks enlarge become necrotic and breaks off from the center. necrotic spots can also merge causing collapse of large areas of the leaf tissue.
GRAY LEAF SPOT
Fungal causal agent/s: Stemphylium spp. including solani, lycopersici, and botrysorum f. sp. lycopersici
Tomato diseases