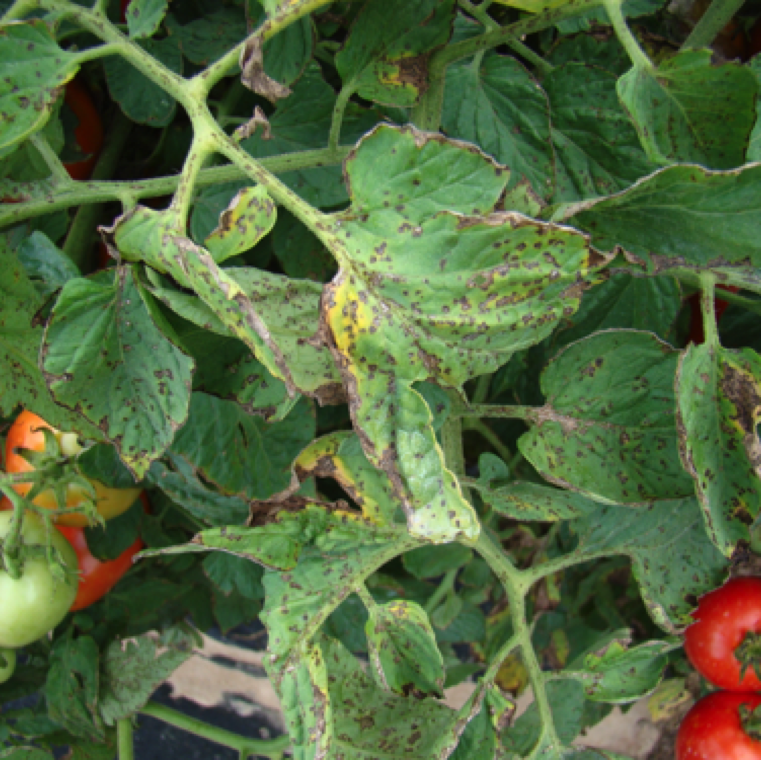
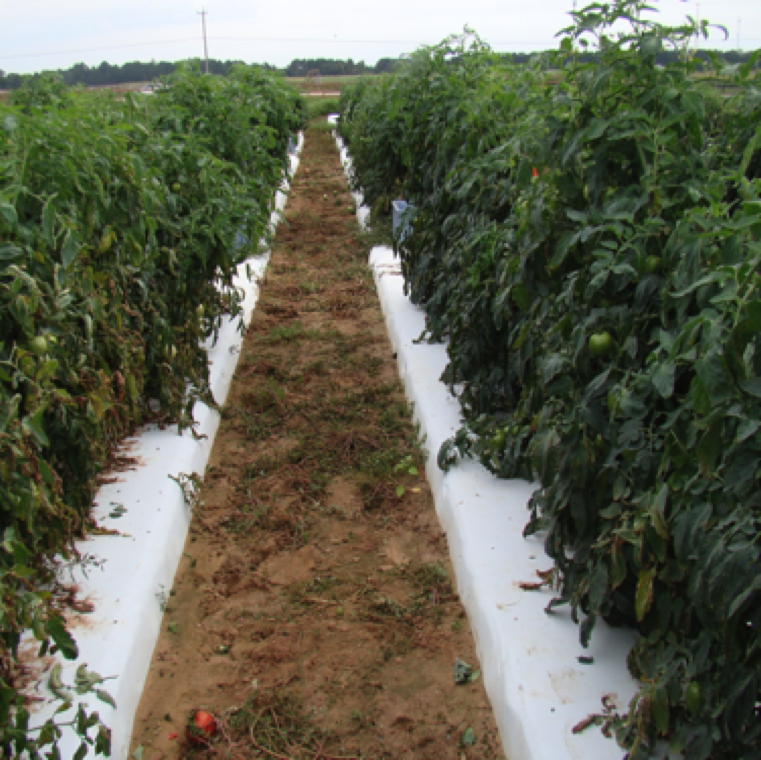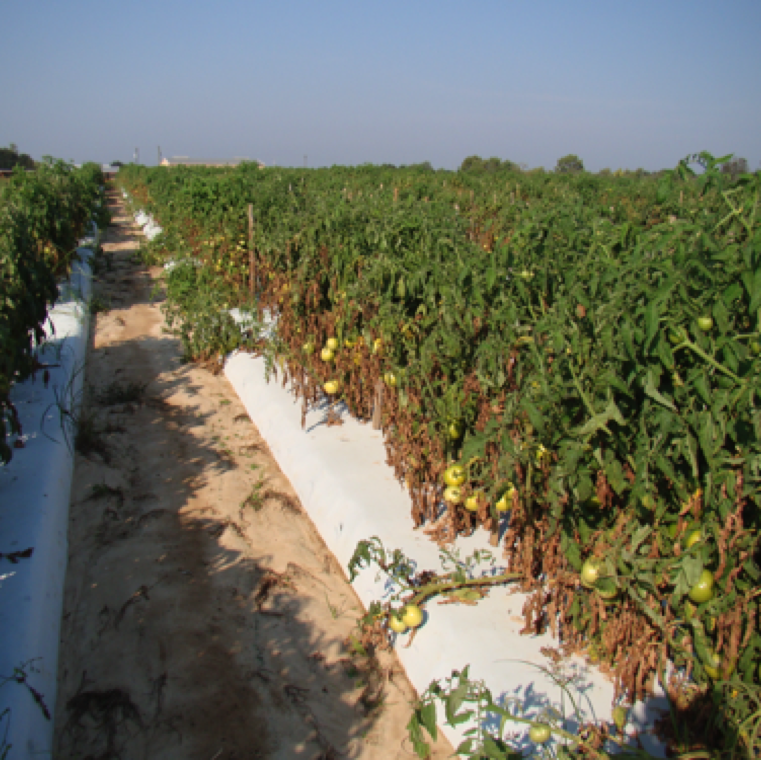


Bacterial spot causes severe leaf lesions and blighting and can significantly affect yield upto 20-50% under extremely wet conditions which is prevalent throughout the year in Florida.

The disease spreads by contaminated seed, transplants, volunteers, and through wind-driven rain. Water-soaking of leaves is the first symptom which can be a symptom of other bacterial diseases.
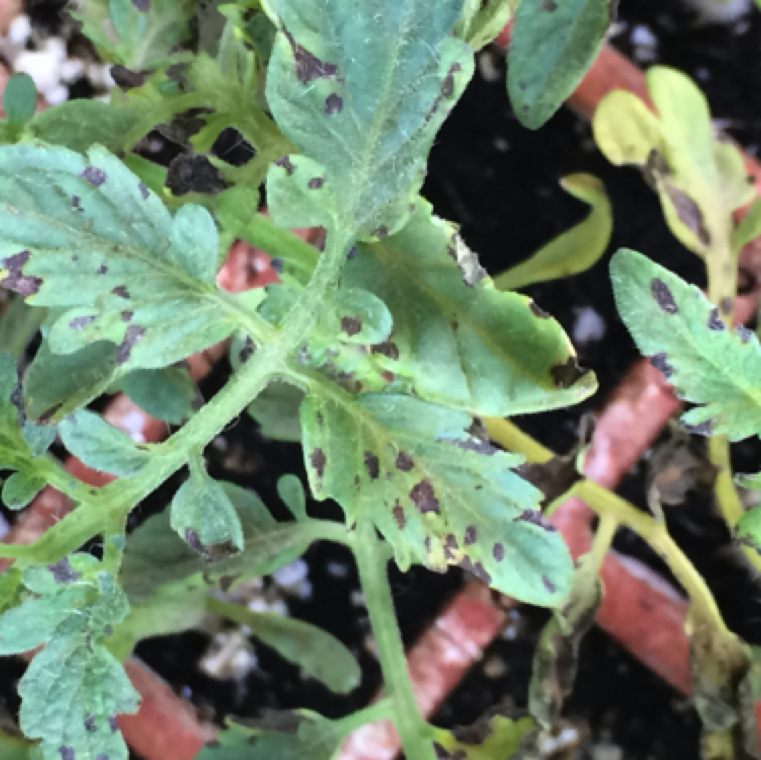

A seedling tray with infected tomato transplants. Avoidance of contaminated transplants is very critical in effective management of the disease through the entire production period.
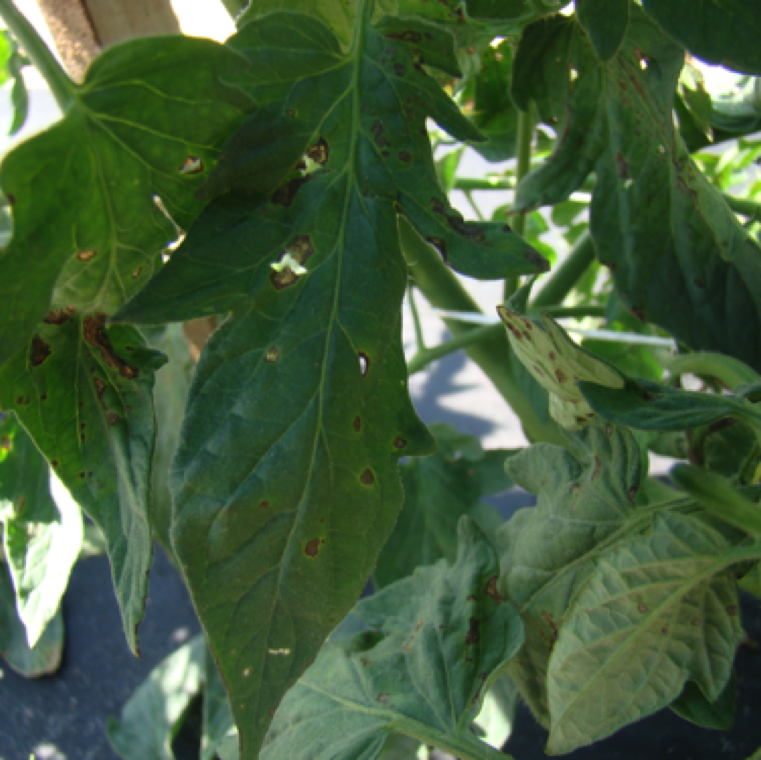

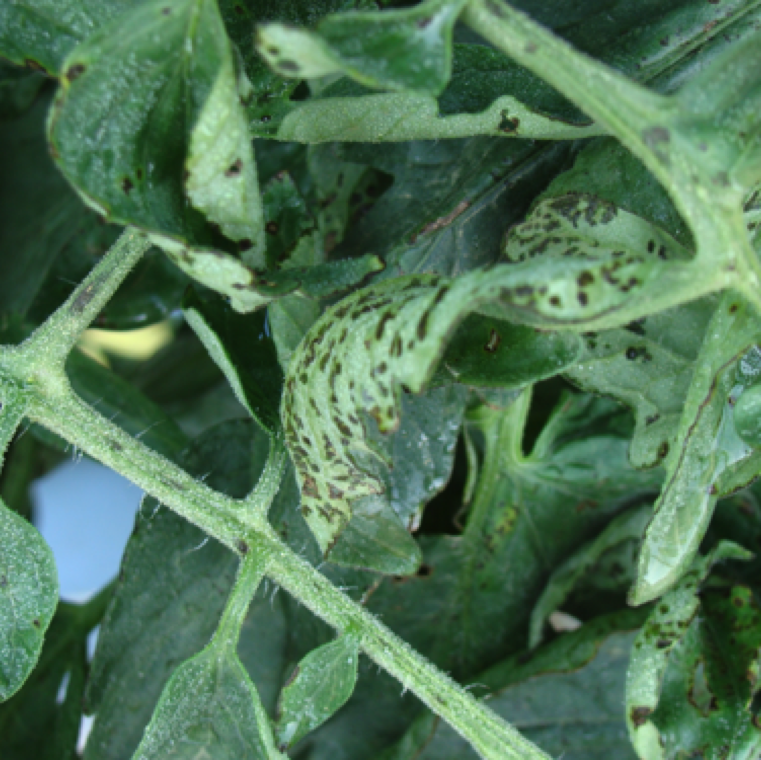
The bacterium enters the plants through natural openings (stomates, hydathodes), or caused by injury to the leaves. Shot-hole like appearance of the lesions is characteristic to the disease.
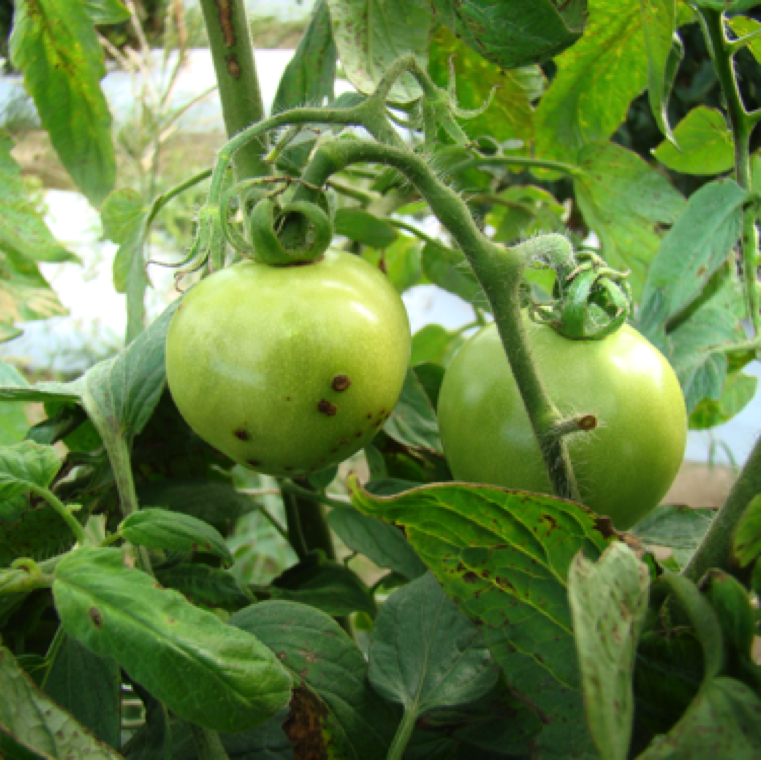

Fruit infections start as a slightly raised blister. A developing lesion may have a faint halo which eventually disappears. The lesions occur primarily due to early infection during flowering.
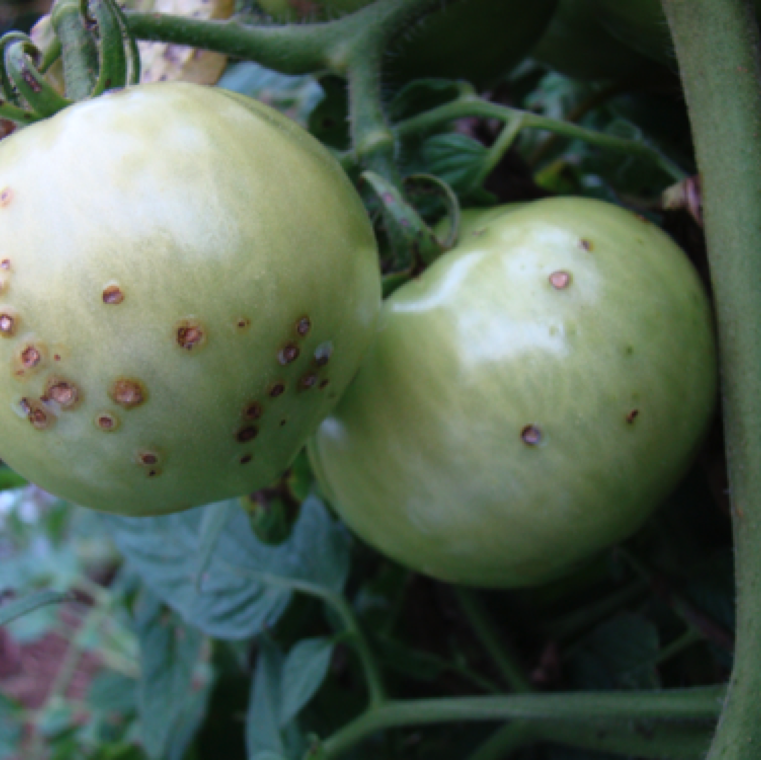

Fruit spots can also be slightly raised and scabby looking. Other diseases including target spot can cause lesions, but tend to be sunken lesions.
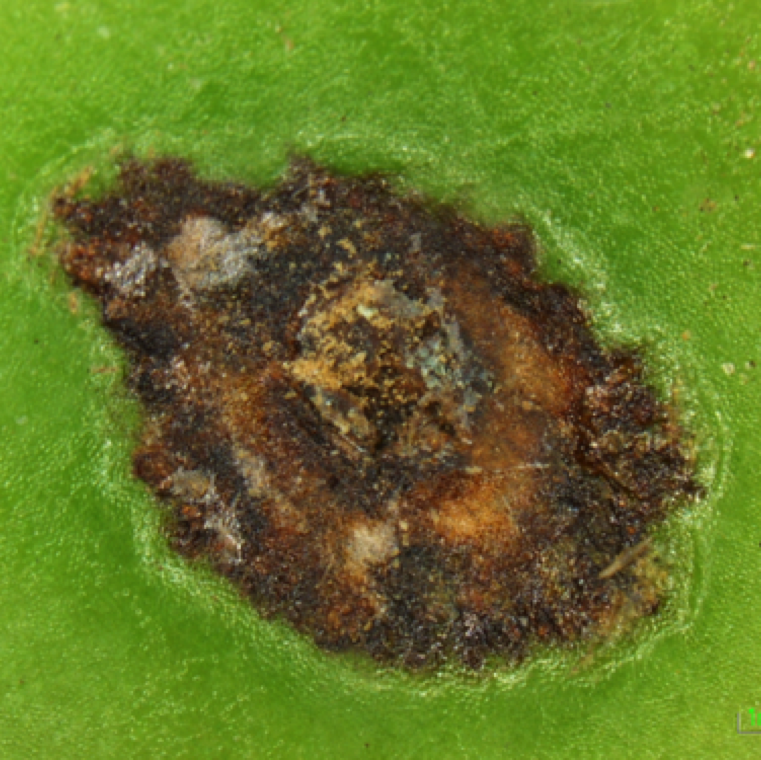

Rain facilitates the movement of the bacterium into the leaflets, petioles, stems and fruit. Mature spots, with or without yellowing have a greasy appearance and can be transparent.
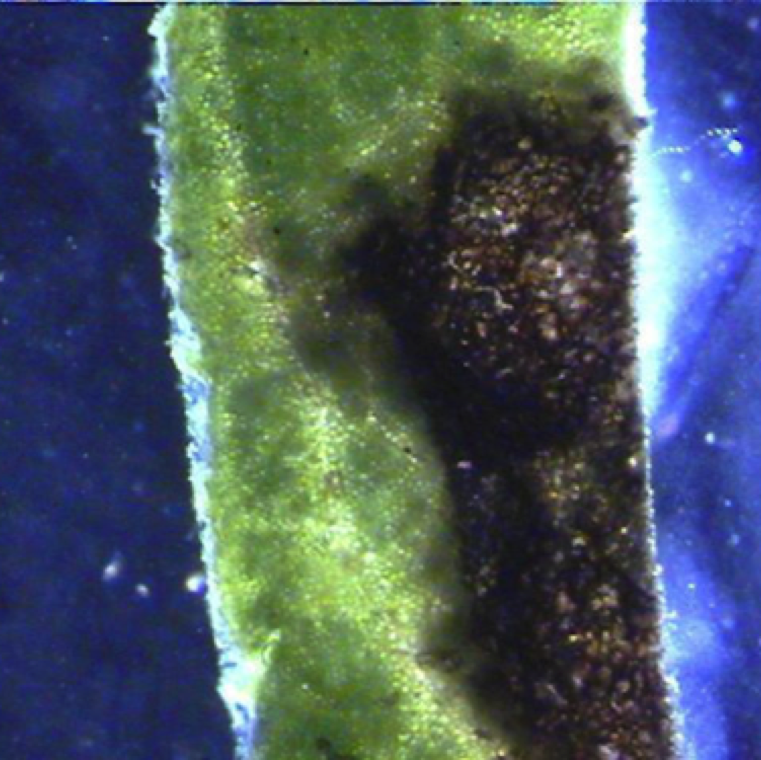
Early blight and target spot symptoms can look similar to bacterial spot. However, the leaves will have a bacterial flow (ooze) from the cut end only in the case of bacterial spot or other bacterial diseases.
Bacterial causal agent: Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria, Other names: X. vesicatoria (Race T1), X. euvesicatoria (Race T2), X. perforans (Race T3, T4), X. gardneri
BACTERIAL SPOT
Tomato diseases

